|
Supplementary code for the Build a Large Language Model From Scratch book by Sebastian Raschka Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch |

|
Llama 3.2 From Scratch (A Standalone Notebook)#
Note: This notebook is an alternative to the standalone-llama32.ipynb notebook but optimized for memory efficiency by using a global mask, cos, and sin. On an A100, based on a 8192 context length, this only uses 3.1 GB (vs 7.07 GB) VRAM.
This notebook is purposefully minimal and focuses on the code to implement the Llama 3.2 1B and 3B LLMs
For a step-by-step guide that explains the individual components and the relationship between GPT, Llama 2, and Llama 3, please see the following companion notebooks:
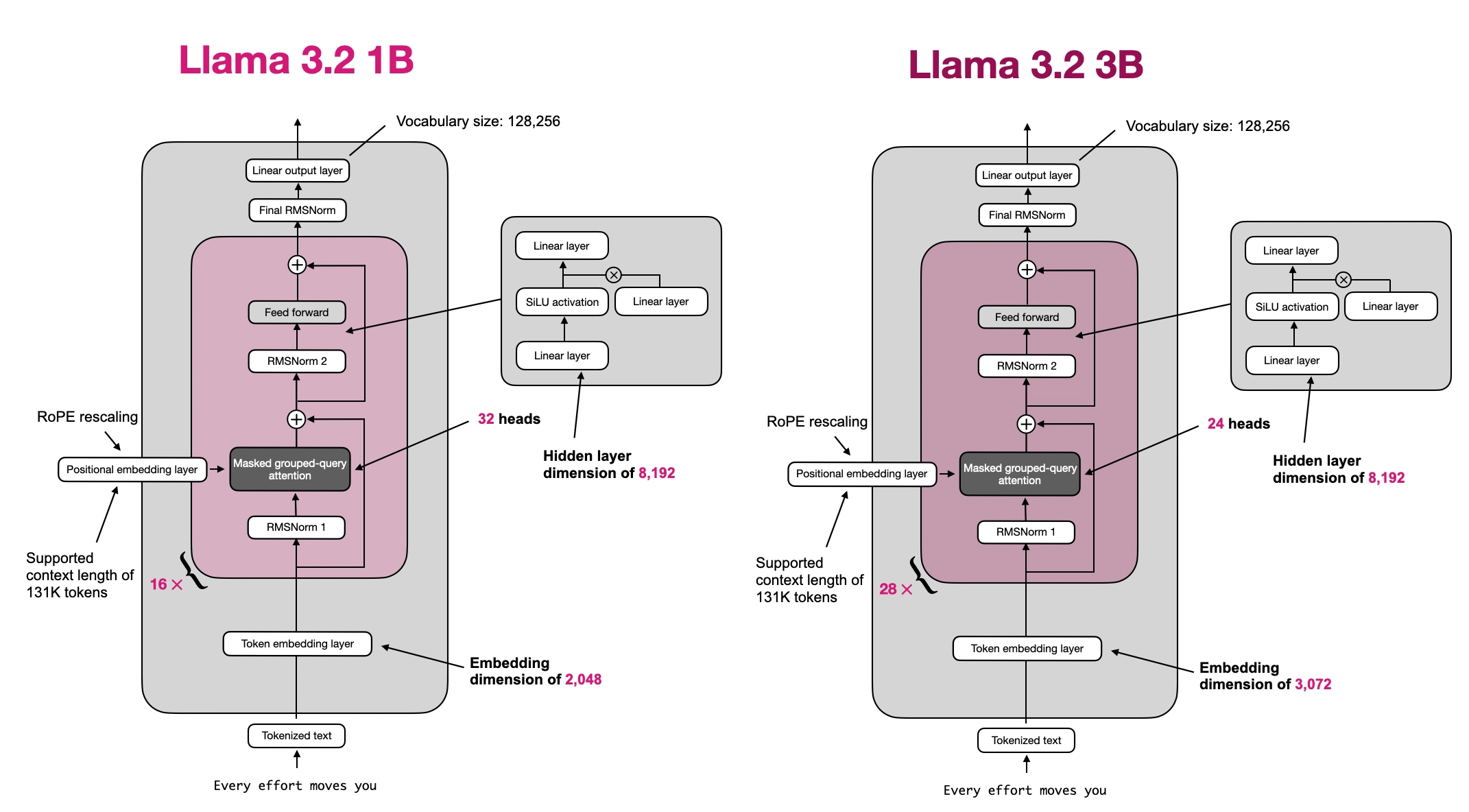
About the code:
all code is my own code, mapping the Llama 3 architecture onto the model code implemented in my Build A Large Language Model (From Scratch) book; the code is released under a permissive open-source Apache 2.0 license (see LICENSE.txt)
the tokenizer code is inspired by the original Llama 3 tokenizer code, which Meta AI used to extend the Tiktoken GPT-4 tokenizer
the RoPE rescaling section is inspired by the _compute_llama3_parameters function in the
transformerslibrary
# pip install -r https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/refs/heads/main/ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/requirements-extra.txt
from importlib.metadata import version
pkgs = [
"blobfile", # to download pretrained weights
"huggingface_hub", # to download pretrained weights
"tiktoken", # to implement the tokenizer
"torch", # to implement the model
]
for p in pkgs:
print(f"{p} version: {version(p)}")
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
PackageNotFoundError Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[2], line 10
3 pkgs = [
4 "blobfile", # to download pretrained weights
5 "huggingface_hub", # to download pretrained weights
6 "tiktoken", # to implement the tokenizer
7 "torch", # to implement the model
8 ]
9 for p in pkgs:
---> 10 print(f"{p} version: {version(p)}")
File /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/lib/python3.10/importlib/metadata/__init__.py:946, in version(distribution_name)
939 def version(distribution_name):
940 """Get the version string for the named package.
941
942 :param distribution_name: The name of the distribution package to query.
943 :return: The version string for the package as defined in the package's
944 "Version" metadata key.
945 """
--> 946 return distribution(distribution_name).version
File /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/lib/python3.10/importlib/metadata/__init__.py:919, in distribution(distribution_name)
913 def distribution(distribution_name):
914 """Get the ``Distribution`` instance for the named package.
915
916 :param distribution_name: The name of the distribution package as a string.
917 :return: A ``Distribution`` instance (or subclass thereof).
918 """
--> 919 return Distribution.from_name(distribution_name)
File /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/lib/python3.10/importlib/metadata/__init__.py:518, in Distribution.from_name(cls, name)
516 return dist
517 else:
--> 518 raise PackageNotFoundError(name)
PackageNotFoundError: No package metadata was found for blobfile
1. Architecture code#
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class FeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfg):
super().__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(cfg["emb_dim"], cfg["hidden_dim"], dtype=cfg["dtype"], bias=False)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(cfg["emb_dim"], cfg["hidden_dim"], dtype=cfg["dtype"], bias=False)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(cfg["hidden_dim"], cfg["emb_dim"], dtype=cfg["dtype"], bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x_fc1 = self.fc1(x)
x_fc2 = self.fc2(x)
x = nn.functional.silu(x_fc1) * x_fc2
return self.fc3(x)
def compute_rope_params(head_dim, theta_base=10_000, context_length=4096, freq_config=None, dtype=torch.float32):
assert head_dim % 2 == 0, "Embedding dimension must be even"
# Compute the inverse frequencies
inv_freq = 1.0 / (theta_base ** (torch.arange(0, head_dim, 2, dtype=dtype)[: (head_dim // 2)].float() / head_dim))
# Frequency adjustments
if freq_config is not None:
low_freq_wavelen = freq_config["original_context_length"] / freq_config["low_freq_factor"]
high_freq_wavelen = freq_config["original_context_length"] / freq_config["high_freq_factor"]
wavelen = 2 * torch.pi / inv_freq
inv_freq_llama = torch.where(
wavelen > low_freq_wavelen, inv_freq / freq_config["factor"], inv_freq
)
smooth_factor = (freq_config["original_context_length"] / wavelen - freq_config["low_freq_factor"]) / (
freq_config["high_freq_factor"] - freq_config["low_freq_factor"]
)
smoothed_inv_freq = (
(1 - smooth_factor) * (inv_freq / freq_config["factor"]) + smooth_factor * inv_freq
)
is_medium_freq = (wavelen <= low_freq_wavelen) & (wavelen >= high_freq_wavelen)
inv_freq_llama = torch.where(is_medium_freq, smoothed_inv_freq, inv_freq_llama)
inv_freq = inv_freq_llama
# Generate position indices
positions = torch.arange(context_length, dtype=dtype)
# Compute the angles
angles = positions[:, None] * inv_freq[None, :] # Shape: (context_length, head_dim // 2)
# Expand angles to match the head_dim
angles = torch.cat([angles, angles], dim=1) # Shape: (context_length, head_dim)
# Precompute sine and cosine
cos = torch.cos(angles)
sin = torch.sin(angles)
return cos, sin
def apply_rope(x, cos, sin):
# x: (batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, head_dim)
batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, head_dim = x.shape
assert head_dim % 2 == 0, "Head dimension must be even"
# Split x into first half and second half
x1 = x[..., : head_dim // 2] # First half
x2 = x[..., head_dim // 2 :] # Second half
# Adjust sin and cos shapes
cos = cos[:seq_len, :].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0) # Shape: (1, 1, seq_len, head_dim)
sin = sin[:seq_len, :].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)
# Apply the rotary transformation
rotated = torch.cat((-x2, x1), dim=-1)
x_rotated = (x * cos) + (rotated * sin)
# It's ok to use lower-precision after applying cos and sin rotation
return x_rotated.to(dtype=x.dtype)
def rescale_theta(theta_old, context_length_old, context_length_new):
scaling_factor = context_length_new / context_length_old
theta_new = theta_old * scaling_factor
return theta_new
class GroupedQueryAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self, d_in, d_out, num_heads,
num_kv_groups,
dtype=None
):
super().__init__()
assert d_out % num_heads == 0, "d_out must be divisible by num_heads"
assert num_heads % num_kv_groups == 0, "num_heads must be divisible by num_kv_groups"
self.d_out = d_out
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.head_dim = d_out // num_heads
self.W_key = nn.Linear(d_in, num_kv_groups * self.head_dim, bias=False, dtype=dtype)
self.W_value = nn.Linear(d_in, num_kv_groups * self.head_dim, bias=False, dtype=dtype)
self.num_kv_groups = num_kv_groups
self.group_size = num_heads // num_kv_groups
self.W_query = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=False, dtype=dtype)
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(d_out, d_out, bias=False, dtype=dtype)
def forward(self, x, mask, cos, sin):
b, num_tokens, d_in = x.shape
queries = self.W_query(x) # Shape: (b, num_tokens, d_out)
keys = self.W_key(x) # Shape: (b, num_tokens, num_kv_groups * head_dim)
values = self.W_value(x) # Shape: (b, num_tokens, num_kv_groups * head_dim)
# Reshape queries, keys, and values
queries = queries.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
keys = keys.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_kv_groups, self.head_dim)
values = values.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_kv_groups, self.head_dim)
# Transpose keys, values, and queries
keys = keys.transpose(1, 2) # Shape: (b, num_heads, num_tokens, head_dim)
values = values.transpose(1, 2) # Shape: (b, num_heads, num_tokens, head_dim)
queries = queries.transpose(1, 2) # Shape: (b, num_query_groups, num_tokens, head_dim)
# Apply RoPE
keys = apply_rope(keys, cos, sin)
queries = apply_rope(queries, cos, sin)
# Expand keys and values to match the number of heads
# Shape: (b, num_heads, num_tokens, head_dim)
keys = keys.repeat_interleave(self.group_size, dim=1) # Shape: (b, num_heads, num_tokens, head_dim)
values = values.repeat_interleave(self.group_size, dim=1) # Shape: (b, num_heads, num_tokens, head_dim)
# For example, before repeat_interleave along dim=1 (query groups):
# [K1, K2]
# After repeat_interleave (each query group is repeated group_size times):
# [K1, K1, K2, K2]
# If we used regular repeat instead of repeat_interleave, we'd get:
# [K1, K2, K1, K2]
# Compute scaled dot-product attention (aka self-attention) with a causal mask
# Shape: (b, num_heads, num_tokens, num_tokens)
attn_scores = queries @ keys.transpose(2, 3) # Dot product for each head
# Use the mask to fill attention scores
attn_scores = attn_scores.masked_fill(mask[:num_tokens, :num_tokens], -torch.inf)
attn_weights = torch.softmax(attn_scores / keys.shape[-1]**0.5, dim=-1)
assert keys.shape[-1] == self.head_dim
# Shape: (b, num_tokens, num_heads, head_dim)
context_vec = (attn_weights @ values).transpose(1, 2)
# Combine heads, where self.d_out = self.num_heads * self.head_dim
context_vec = context_vec.reshape(b, num_tokens, self.d_out)
context_vec = self.out_proj(context_vec) # optional projection
return context_vec
class TransformerBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfg):
super().__init__()
self.att = GroupedQueryAttention(
d_in=cfg["emb_dim"],
d_out=cfg["emb_dim"],
num_heads=cfg["n_heads"],
num_kv_groups=cfg["n_kv_groups"],
dtype=cfg["dtype"]
)
self.ff = FeedForward(cfg)
self.norm1 = nn.RMSNorm(cfg["emb_dim"], eps=1e-5, dtype=cfg["dtype"])
self.norm2 = nn.RMSNorm(cfg["emb_dim"], eps=1e-5, dtype=cfg["dtype"])
def forward(self, x, mask, cos, sin):
# Shortcut connection for attention block
shortcut = x
x = self.norm1(x)
x = self.att(x, mask, cos, sin) # Shape [batch_size, num_tokens, emb_size]
x = x + shortcut # Add the original input back
# Shortcut connection for feed-forward block
shortcut = x
x = self.norm2(x)
x = self.ff(x)
x = x + shortcut # Add the original input back
return x
class Llama3Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfg):
super().__init__()
# Main model parameters
self.tok_emb = nn.Embedding(cfg["vocab_size"], cfg["emb_dim"], dtype=cfg["dtype"])
self.trf_blocks = nn.ModuleList( # ModuleList since Sequential can only accept one input, and we need `x, mask, cos, sin`
[TransformerBlock(cfg) for _ in range(cfg["n_layers"])]
)
self.final_norm = nn.RMSNorm(cfg["emb_dim"], eps=1e-5, dtype=cfg["dtype"])
self.out_head = nn.Linear(cfg["emb_dim"], cfg["vocab_size"], bias=False, dtype=cfg["dtype"])
# Reusuable utilities
self.register_buffer(
"mask", torch.triu(torch.ones(cfg["context_length"], cfg["context_length"]), diagonal=1).bool(),
persistent=False
)
cfg["rope_base"] = rescale_theta(
cfg["rope_base"],
cfg["orig_context_length"],
cfg["context_length"]
)
cos, sin = compute_rope_params(
head_dim=cfg["emb_dim"] // cfg["n_heads"],
theta_base=cfg["rope_base"],
context_length=cfg["context_length"],
freq_config=cfg["rope_freq"]
)
self.register_buffer("cos", cos)
self.register_buffer("sin", sin)
self.cfg = cfg
def forward(self, in_idx):
# Forward pass
tok_embeds = self.tok_emb(in_idx)
x = tok_embeds
for block in self.trf_blocks:
x = block(x, self.mask, self.cos, self.sin)
x = self.final_norm(x)
logits = self.out_head(x.to(self.cfg["dtype"]))
return logits
2. Initialize model#
The remainder of this notebook uses the Llama 3.2 1B model; to use the 3B model variant, just uncomment the second configuration file in the following code cell
# Llama 3.2 1B
LLAMA32_CONFIG = {
"vocab_size": 128_256, # Vocabulary size
"context_length": 8192, # Maximum context length to use (reduced to save memory)
"orig_context_length": 131_072, # Context length that was used to train the model
"emb_dim": 2048, # Embedding dimension
"n_heads": 32, # Number of attention heads
"n_layers": 16, # Number of layers
"hidden_dim": 8192, # Size of the intermediate dimension in FeedForward
"n_kv_groups": 8, # Key-Value groups for grouped-query attention
"rope_base": 500_000.0, # The base in RoPE's "theta"
"dtype": torch.bfloat16, # Lower-precision dtype to reduce memory usage
"rope_freq": { # RoPE frequency scaling
"factor": 32.0,
"low_freq_factor": 1.0,
"high_freq_factor": 4.0,
"original_context_length": 8192,
}
}
# Llama 3.2 3B
# LLAMA32_CONFIG = {
# "vocab_size": 128_256, # Vocabulary size
# "context_length": 8192, # Maximum context length to use (reduced to save memory)
# "orig_context_length": 131_072, # Context length that was used to train the model
# "emb_dim": 3072, # Embedding dimension
# "n_heads": 24, # Number of attention heads
# "n_layers": 28, # Number of layers
# "hidden_dim": 8192, # Size of the intermediate dimension in FeedForward
# "n_kv_groups": 8, # Key-Value groups for grouped-query attention
# "rope_base": 500_000.0, # The base in RoPE's "theta"
# "dtype": torch.bfloat16, # Lower-precision dtype to reduce memory usage
# "rope_freq": { # RoPE frequency scaling
# "factor": 32.0,
# "low_freq_factor": 1.0,
# "high_freq_factor": 4.0,
# "original_context_length": 8192,
# }
# }
LLAMA_SIZE_STR = "1B" if LLAMA32_CONFIG["emb_dim"] == 2048 else "3B"
model = Llama3Model(LLAMA32_CONFIG)
The following is expected to print True to confirm buffers are reused instead of being (wastefully) recreated:
total_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters())
print(f"Total number of parameters: {total_params:,}")
# Account for weight tying
total_params_normalized = total_params - model.tok_emb.weight.numel()
print(f"\nTotal number of unique parameters: {total_params_normalized:,}")
Total number of parameters: 1,498,482,688
Total number of unique parameters: 1,235,814,400
def model_memory_size(model, input_dtype=torch.float32):
total_params = 0
total_grads = 0
for param in model.parameters():
# Calculate total number of elements per parameter
param_size = param.numel()
total_params += param_size
# Check if gradients are stored for this parameter
if param.requires_grad:
total_grads += param_size
# Calculate buffer size (non-parameters that require memory)
total_buffers = sum(buf.numel() for buf in model.buffers())
# Size in bytes = (Number of elements) * (Size of each element in bytes)
# We assume parameters and gradients are stored in the same type as input dtype
element_size = torch.tensor(0, dtype=input_dtype).element_size()
total_memory_bytes = (total_params + total_grads + total_buffers) * element_size
# Convert bytes to gigabytes
total_memory_gb = total_memory_bytes / (1024**3)
return total_memory_gb
print(f"float32 (PyTorch default): {model_memory_size(model, input_dtype=torch.float32):.2f} GB")
print(f"bfloat16: {model_memory_size(model, input_dtype=torch.bfloat16):.2f} GB")
float32 (PyTorch default): 11.42 GB
bfloat16: 5.71 GB
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = torch.device("cuda")
elif torch.backends.mps.is_available():
device = torch.device("mps")
else:
device = torch.device("cpu")
model.to(device);
3. Load tokenizer#
import os
from pathlib import Path
import tiktoken
from tiktoken.load import load_tiktoken_bpe
class Tokenizer:
def __init__(self, model_path):
assert os.path.isfile(model_path), f"Model file {model_path} not found"
mergeable_ranks = load_tiktoken_bpe(model_path)
self.special_tokens = {
"<|begin_of_text|>": 128000,
"<|end_of_text|>": 128001,
"<|start_header_id|>": 128006,
"<|end_header_id|>": 128007,
"<|eot_id|>": 128009,
}
self.special_tokens.update({
f"<|reserved_{i}|>": 128002 + i for i in range(256) if (128002 + i) not in self.special_tokens.values()
})
self.model = tiktoken.Encoding(
name=Path(model_path).name,
pat_str=r"(?i:'s|'t|'re|'ve|'m|'ll|'d)|[^\r\n\p{L}\p{N}]?\p{L}+|\p{N}{1,3}| ?[^\s\p{L}\p{N}]+[\r\n]*|\s*[\r\n]+|\s+(?!\S)|\s+",
mergeable_ranks=mergeable_ranks,
special_tokens=self.special_tokens
)
def encode(self, text, bos=False, eos=False, allowed_special=set(), disallowed_special=()):
if bos:
tokens = [self.special_tokens["<|begin_of_text|>"]]
else:
tokens = []
tokens += self.model.encode(text, allowed_special=allowed_special, disallowed_special=disallowed_special)
if eos:
tokens.append(self.special_tokens["<|end_of_text|>"])
return tokens
def decode(self, tokens):
return self.model.decode(tokens)
class ChatFormat:
def __init__(self, tokenizer):
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
def encode_header(self, message):
tokens = []
tokens.append(self.tokenizer.special_tokens["<|start_header_id|>"])
tokens.extend(self.tokenizer.encode(message["role"], bos=False, eos=False))
tokens.append(self.tokenizer.special_tokens["<|end_header_id|>"])
tokens.extend(self.tokenizer.encode("\n\n", bos=False, eos=False))
return tokens
def encode(self, text):
message = {
"role": "user",
"content": text
}
tokens = self.encode_header(message)
tokens.extend(
self.tokenizer.encode(message["content"].strip(), bos=False, eos=False)
)
tokens.append(self.tokenizer.special_tokens["<|eot_id|>"])
return tokens
def decode(self, token_ids):
return self.tokenizer.decode(token_ids)
Please note that Meta AI requires that you accept the Llama 3.2 licensing terms before you can download the files; to do this, you have to create a Hugging Face Hub account and visit the meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B repository to accept the terms
Next, you will need to create an access token; to generate an access token with READ permissions, click on the profile picture in the upper right and click on “Settings”
Then, create and copy the access token so you can copy & paste it into the next code cell

from huggingface_hub import login
login()
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
tokenizer_file_path = hf_hub_download(
repo_id=f"meta-llama/Llama-3.2-{LLAMA_SIZE_STR}-Instruct",
filename="original/tokenizer.model",
local_dir=f"Llama-3.2-{LLAMA_SIZE_STR}-Instruct"
)
tokenizer = Tokenizer(tokenizer_file_path)
chat_tokenizer = ChatFormat(tokenizer)
4. Load pretrained weights#
def assign(left, right, tensor_name="unknown"):
if left.shape != right.shape:
raise ValueError(f"Shape mismatch in tensor '{tensor_name}'. Left: {left.shape}, Right: {right.shape}")
if isinstance(right, torch.Tensor):
return torch.nn.Parameter(right.clone().detach())
else:
return torch.nn.Parameter(torch.tensor(right))
def load_weights_into_llama(model, param_config, params):
model.tok_emb.weight = assign(model.tok_emb.weight, params["model.embed_tokens.weight"], "model.embed_tokens.weight")
for l in range(param_config["n_layers"]):
# Load attention weights
model.trf_blocks[l].att.W_query.weight = assign(
model.trf_blocks[l].att.W_query.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.q_proj.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.q_proj.weight"
)
model.trf_blocks[l].att.W_key.weight = assign(
model.trf_blocks[l].att.W_key.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.k_proj.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.k_proj.weight"
)
model.trf_blocks[l].att.W_value.weight = assign(
model.trf_blocks[l].att.W_value.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.v_proj.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.v_proj.weight"
)
model.trf_blocks[l].att.out_proj.weight = assign(
model.trf_blocks[l].att.out_proj.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.o_proj.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.o_proj.weight"
)
model.trf_blocks[l].norm1.weight = assign(
model.trf_blocks[l].norm1.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.input_layernorm.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.input_layernorm.weight"
)
# Load FeedForward weights
model.trf_blocks[l].ff.fc1.weight = assign(
model.trf_blocks[l].ff.fc1.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.gate_proj.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.gate_proj.weight"
)
model.trf_blocks[l].ff.fc2.weight = assign(
model.trf_blocks[l].ff.fc2.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.up_proj.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.up_proj.weight"
)
model.trf_blocks[l].ff.fc3.weight = assign(
model.trf_blocks[l].ff.fc3.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.down_proj.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.down_proj.weight"
)
model.trf_blocks[l].norm2.weight = assign(
model.trf_blocks[l].norm2.weight,
params[f"model.layers.{l}.post_attention_layernorm.weight"],
f"model.layers.{l}.post_attention_layernorm.weight"
)
# Load output layer weights
model.final_norm.weight = assign(model.final_norm.weight, params["model.norm.weight"], "model.norm.weight")
if "lm_head.weight" in params.keys():
model.out_head.weight = assign(model.out_head.weight, params["lm_head.weight"], "lm_head.weight")
else:
model.out_head.weight = assign(model.out_head.weight, params["model.embed_tokens.weight"], "model.embed_tokens.weight")
print("Model uses weight tying.")
from safetensors.torch import load_file
if LLAMA_SIZE_STR == "1B":
weights_file = hf_hub_download(
repo_id=f"meta-llama/Llama-3.2-{LLAMA_SIZE_STR}-Instruct",
filename="model.safetensors",
local_dir=f"Llama-3.2-{LLAMA_SIZE_STR}-Instruct"
)
combined_weights = load_file(weights_file)
else:
combined_weights = {}
for i in range(1, 3):
weights_file = hf_hub_download(
repo_id=f"meta-llama/Llama-3.2-{LLAMA_SIZE_STR}-Instruct",
filename=f"model-0000{i}-of-00002.safetensors",
local_dir=f"Llama-3.2-{LLAMA_SIZE_STR}-Instruct"
)
current_weights = load_file(weights_file)
combined_weights.update(current_weights)
load_weights_into_llama(model, LLAMA32_CONFIG, combined_weights)
model.to(device)
del combined_weights # free up memory
Model uses weight tying.
print("Weight tying:", torch.equal(model.tok_emb.weight, model.out_head.weight))
Weight tying: True
5. Generate text#
def text_to_token_ids(text, tokenizer):
encoded = tokenizer.encode(text)
encoded_tensor = torch.tensor(encoded).unsqueeze(0) # add batch dimension
return encoded_tensor
def token_ids_to_text(token_ids, tokenizer):
flat = token_ids.squeeze(0) # remove batch dimension
return tokenizer.decode(flat.tolist())
def generate(model, idx, max_new_tokens, context_size, temperature=0.0, top_k=None, eos_id=None):
# For-loop is the same as before: Get logits, and only focus on last time step
for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
idx_cond = idx[:, -context_size:]
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(idx_cond)
logits = logits[:, -1, :]
# New: Filter logits with top_k sampling
if top_k is not None:
# Keep only top_k values
top_logits, _ = torch.topk(logits, top_k)
min_val = top_logits[:, -1]
logits = torch.where(logits < min_val, torch.tensor(float('-inf')).to(logits.device), logits)
# New: Apply temperature scaling
if temperature > 0.0:
logits = logits / temperature
# Apply softmax to get probabilities
probs = torch.softmax(logits, dim=-1) # (batch_size, context_len)
# Sample from the distribution
idx_next = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1) # (batch_size, 1)
# Otherwise same as before: get idx of the vocab entry with the highest logits value
else:
idx_next = torch.argmax(logits, dim=-1, keepdim=True) # (batch_size, 1)
if idx_next == eos_id: # Stop generating early if end-of-sequence token is encountered and eos_id is specified
break
# Same as before: append sampled index to the running sequence
idx = torch.cat((idx, idx_next), dim=1) # (batch_size, num_tokens+1)
return idx
import time
PROMPT = "What do llamas eat?"
torch.manual_seed(123)
start = time.time()
token_ids = generate(
model=model,
idx=text_to_token_ids(PROMPT, chat_tokenizer).to(device),
max_new_tokens=150,
context_size=LLAMA32_CONFIG["context_length"],
top_k=1,
temperature=0.
)
print(f"Time: {time.time() - start:.2f} sec")
if torch.cuda.is_available():
max_mem_bytes = torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated()
max_mem_gb = max_mem_bytes / (1024 ** 3)
print(f"Max memory allocated: {max_mem_gb:.2f} GB")
output_text = token_ids_to_text(token_ids, tokenizer)
def clean_text(text, header_end="assistant<|end_header_id|>\n\n"):
# Find the index of the first occurrence of "<|end_header_id|>"
index = text.find(header_end)
if index != -1:
# Return the substring starting after "<|end_header_id|>"
return text[index + len(header_end):].strip() # Strip removes leading/trailing whitespace
else:
# If the token is not found, return the original text
return text
print("\n\nOutput text:\n\n", clean_text(output_text))
Time: 19.49 sec
Output text:
Llamas are herbivores, which means they primarily eat plants and plant-based foods. Their diet typically consists of:
1. Grasses: Llamas love to graze on various types of grasses, including tall grasses and short grasses.
2. Hay: Llamas also eat hay, which is a dry, compressed form of grass or other plants.
3. Alfalfa: Alfalfa is a legume that is commonly used as a hay substitute in llama feed.
4. Other plants: Llamas will also eat other plants, such as clover, dandelions, and wild grasses.
It's worth noting that the specific diet of llamas can vary depending on factors such as
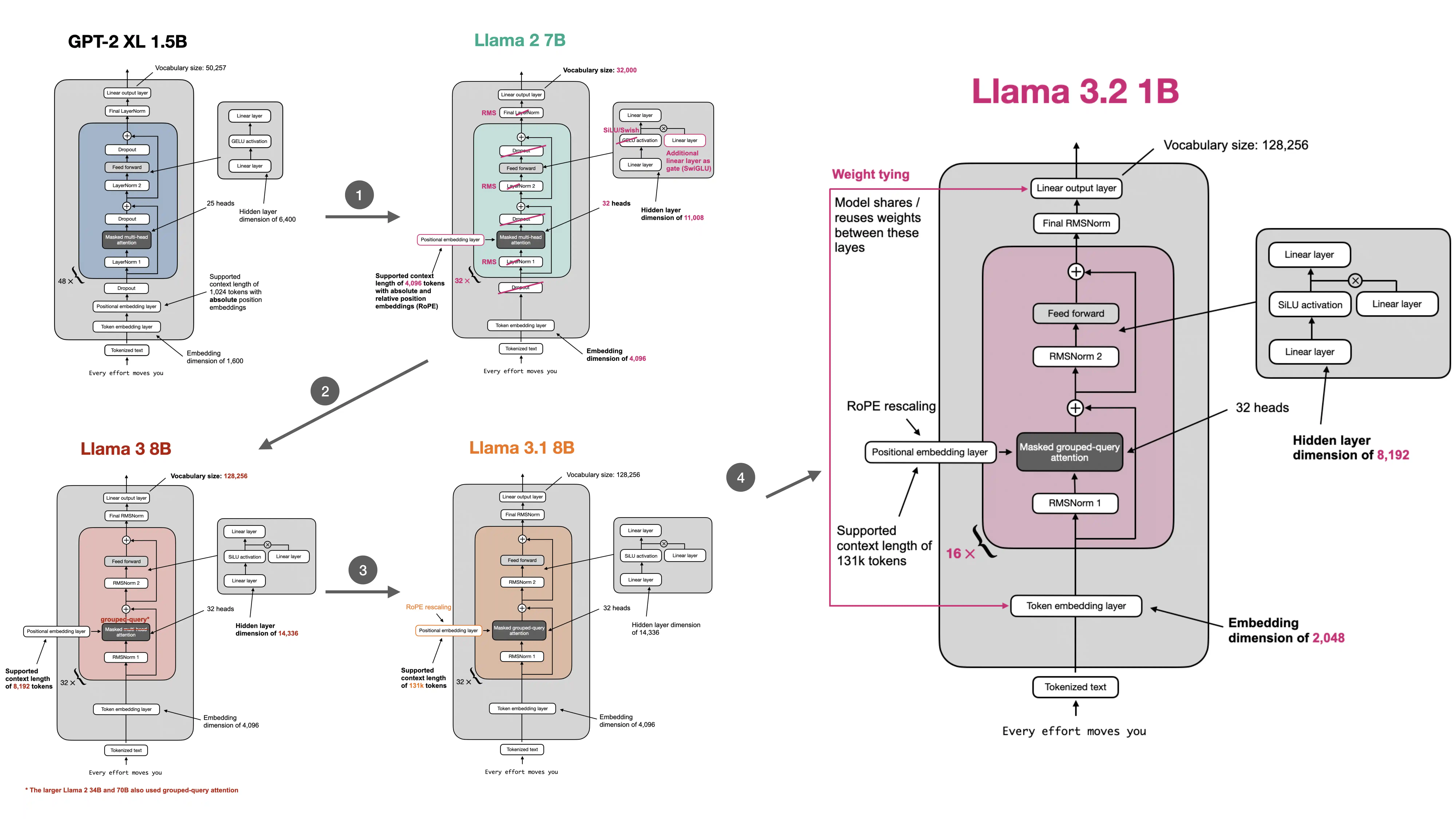
What’s next?#
The notebook was kept purposefully minimal; if you are interested in additional explanation about the individual components, check out the following two companion notebooks:
For those interested in a comprehensive guide on building a large language model from scratch and gaining a deeper understanding of its mechanics, you might like my Build a Large Language Model (From Scratch)

